Latest
News
Automotive Electro-Mechanical Relays Types / Faults / Diagnosis
May 2013
We need to relay this important information
With the amount of electrical components and controls now fitted to the modern vehicle, it is important that the targeted load is supplied with the necessary voltage / current as required to ensure continuous, uninterrupted operation.
That is, to reduce voltage drop to the component during broad temperature changes and high vibration in all climate operation. As an example, whether it’s a radiator cooling fan, an air conditioning compressor or a starter motor, any relay interruption may cause at least an uncomfortable journey or possibly a trip on the tow truck. All this from a low cost, readily available, easily tested and replaced, small but important component that gets generally verbally abused when it fails. Ask me how I know.
Let’s look at the types of vehicle relays and the importance of fitting the correct replacement
Typical commonly used automotive types.
Mini Relays – electromechanically operated contact switches. May be 4 pin / 5 pin or 6 pin configuration.
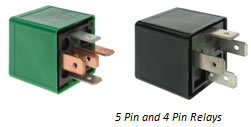
The 4 pin configuration may either be:
A Normally open (NO) relay where the internal mechanical contacts are held open when the relay is in a disconnected state. The contacts close when activated. This is the most common type found on the vehicle. A specifically produced power relay may resemble this unit but is manufactured for switching nominal current of 50A or more, making them suitable as operating relays for starting motors, glow plug operation, motor relay for antilock braking systems, to name a few.
A normally closed (NC) relay where the internal mechanical contacts are held closed when the relay is in a disconnected state.
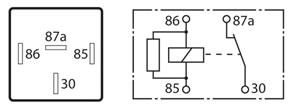
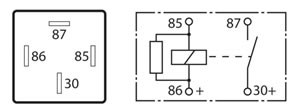
The 5 pin configuration may be:
A Change over relay where 2 sets of contacts are used with one set normally open and the other set normally closed. These of course will alternate once the relay is activated. This type of relay will generally display 2 current ratings (for each contact circuit) and it is important that a replacement relay unit is matched to the original relay specifications.
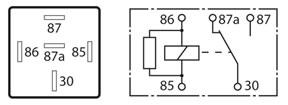
A Normally open, dual output 5 pin relay
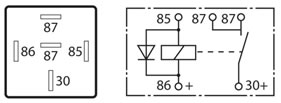
But wait there’s more.
Even on these common relay types there are more variations and features and fitting any old relay is not an option.
- Resistor protected or Diode Protected
- Terminals 36 and 86 exchanged
- Amperage variations and variations in contact material.
Micro Relays
These units are ideal, due to their size, for space restricted areas. The micro relays vary in pin configuration to the mini relays but are still available in 4 and 5 pin with similar variations and features.
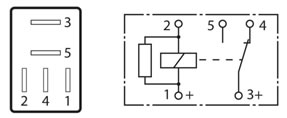
Pin identification may vary to the mini relays as follows.

Faults/ Diagnosis/Testing.
The relay may intermittently fail under certain conditions or fail totally. This may be confused with harness or socket terminal faults so it is important to correctly verify the fault.
Simple test equipment is available to quickly identify some circuit or relay faults and carry out time saving quick tests.

We need to get excited about it.
A common occurring vehicle system fault is the lack of relay winding excitation that can stop the relay functioning and can cause the vehicle to stall. A typical example may be the petrol fuel pump relay which switches off whilst driving that is caused by a fault in the ECM and not in the relay itself.
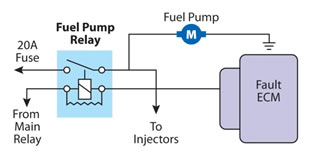
Renewing the relay and sending the vehicle on its way is not a thorough test. Unfortunately, by the time the Technician has been called out and proceeds to carry out any tests on the vehicle the ECM has cooled down and may function normally. Thorough testing again is required to pin point the area of concern.
Simple test equipment again may assist the Technician to carry out this task. Bridging relay socket pins for the inexperienced or semi educated may result in damage or unrepairable damage to the fuel pump control circuit in the ECM. You may be surprised on how many times this has occurred. Then again you may not!
|