|
Latest News
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
As cars have become more sophisticated, the way many functions of the vehicle are controlled and monitored has evolved. With the inevitable arrival of electric vehicles to the workshop it is more important than ever to understand basic electrical principles. In striving for efficiency in all things electric to allow for maximum performance and comfort while minimising the energy use so as to minimise the impact to the range on an electric vehicle and emissions on an ICE vehicle.
Pulse Width Modulation is one control method that crosses over from ICE to EV.
What is Pulse Width Modulation?
Pulse Width Modulation is used across many disciplines of electrical engineering to provide efficient and variable control of an electrical component. PWM is a way to control an analogue device with a digital output. By switching the supply voltage to a component on and off very quickly the average voltage to that component can be varied. The longer the on time the higher the average voltage, the shorter the on time the lower the average voltage. The frequency doesn’t alter, just the amount of on time. If you attached a voltmeter to the component being controlled you would read the average voltage. You can only see the switching using an oscilloscope. Duty cycle is the term used to indicate the amount of on time. If the pulse is on for half the time and off for half the time this would be expressed as a 50% duty cycle. If it was on for 25% of the time that would be a 25% duty cycle.
Pulse Width Modulated Waveforms
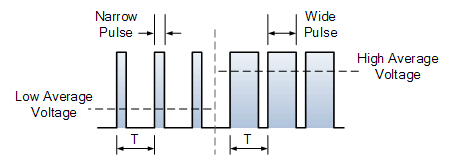
Image source www.electronics-tutorials.ws/blog/pulse-width-modulation
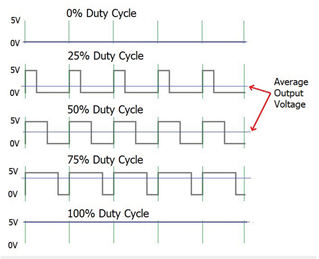
Image source www.circuitdigest.com/tutorial
We know that a fan speed can be controlled by resistors placed in series with a fan motor to give various speed settings. This creates heat at the resistors which is loss of energy and is limiting as to the number of speeds available. On Climate Control the fan has infinite speed control by using PWM. Instead of reducing the voltage supplied to the motor by adding resistor in series PWM turns the supply voltage on and off very quickly allowing full control of the motor speed. The only loss of energy is a small loss across the switching transistor
Where is PWM used in cars?
Let’s consider a mechanical water pump on an internal combustion engine. The pump is driven whenever the engine is running and hence adding load to the engine regardless of whether or not the engine needs cooling. If we use an electric water pump and control it using PWM not only can we control engine temperature by controlling the speed of the pump but we can leave the pump turned off whenever cooling is not required. If we now transfer this to EV’s we can control the temperature at the battery (RESS - rechargeable energy storage system) to the ideal temperature for maximum efficiency.

EWP-014
Modern fuel systems use demand based fuel supply where the control unit controls the fuel pump using PWM. In contrast to regulated fuel supply, only the required amount of fuel is being pumped. This reduces power consumption and saves fuel.
As well as the above other systems that are controlled by PWM include Electronic Throttle Bodies, Electric Trailer Brakes, Interior lights and Exterior lights, EGR’s and many others.
Testing.
To get a true indication of the correct operation of a circuit controlled by PWM the signal is best viewed with an oscilloscope or suitable scan tool. Manufacturer’s instructions should always be referred to and followed.
Many components controlled by PWM can be bench tested using the EQP-115 EGR/Throttle Body and Actuator tester. This tester provides a variable pulse that can drive DC electric motors, lights, fans, throttle bodies, EGR’s etc.

Here at PAT we’re constantly working with OE suppliers and vehicle manufacturers to ensure we stay up to date with the latest technologies. This constant research and development allows PAT to have the parts and technical knowledge available to our clients as transportation evolves.
|