|
|
|
|
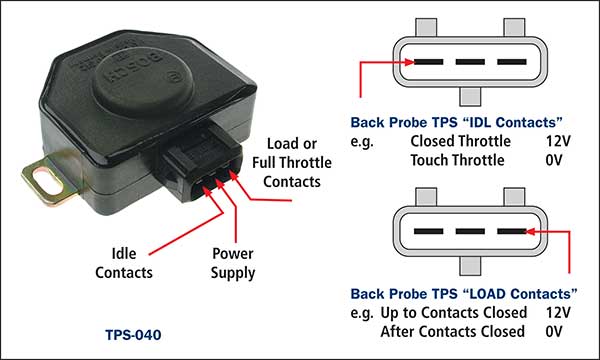
Latest News Throttle Position Sensors (TPS) What a technician needs to know about diagnosing, testing and replacing TPS switches and sensors on a variety of vehicles. With a great variety of TPS types fitted to vehicles commonly found in a typical work shop, it is important for the technician to be familiar with the operating and testing principals as testing procedures may vary between types. The effects on a vehicle’s operation whilst having a faulty TPS fitted will generally vary for systems with or without electronic throttle control. To better understand the correct test procedures, we need to first look at the selections and their operating principles. TPS with contacts only. This unit generally incorporates 2 sets of contacts:
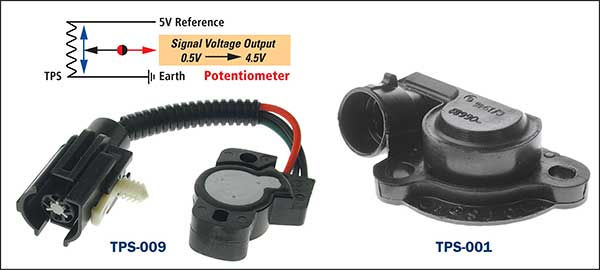
Potentiometer type TPS (3 wire) This common type unit comes in many forms, but the operating principle remains the same. The throttle valve position is monitored from minimum throttle position (idle) and all the way to full throttle position and is generally represented as an analogue varying voltage from approx. 0.5V at idle and peaking near the reference supply voltage. (approx. 4.5V). A suitable oscilloscope is the recommended test equipment for this type of TPS. A suitable scanner can also be utilised for accurate testing. This potentiometer voltage signal is utilised by the ECU as a driver demand and is a very Important signal that greatly affects engine operation.
Combination of contact and potentiometer type TPS. This is a potentiometer type TPS with an integrated idle contact to monitor the ‘foot off accelerator idle position. This type is identified by an extra 4th pin, however not all 4 pin TPS units are of this type. Note it is like the “contact type' TPS and the idle contact must be closed during the “foot off” accelerator idle condition and opens as the butterfly just moves from the rest position.
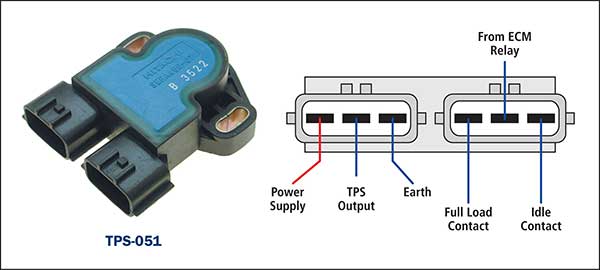
Combination of potentiometer and contacts. This is a potentiometer type TPS with integrated idle and full load contacts, generally identified by two separate 3 pin connector plugs.
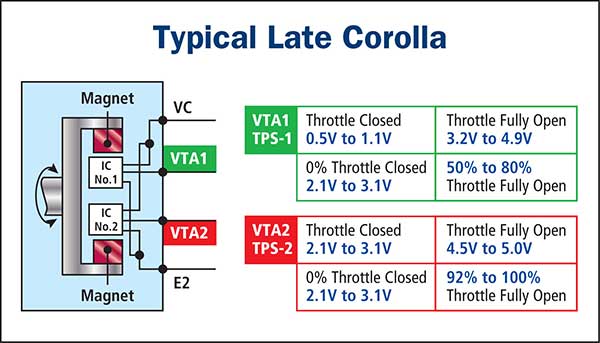
Dual Potentiometer type TPS as fitted to BA / BF Falcon Electronic Throttle Body. This dual potentiometer type TPS is replaceable as a separate unit. Most electronic throttle bodies incorporate an integrated TPS and cannot be renewed separately. Both TPS units utilise a common power supply as well as a common ground.
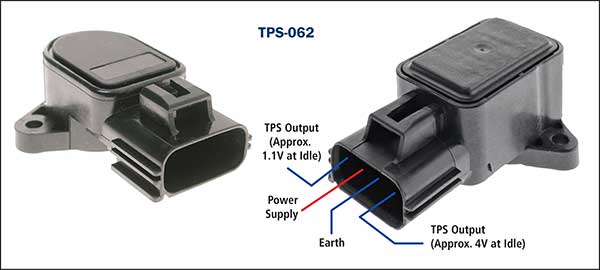
It is critical for correct engine management operation that the TPS is set correctly. An incorrectly adjusted TPS can cause many performance irregularities. Wiring Configuration Many of the TPS units may look similar externally but vary dramatically internally. An incorrect unit fitted may cause ECU damage, with definite performance problems. NOTE: Many vehicles incorporate an engine flood mode as one of its engine controls. This allows for an ECU to switch off the injector pulses during cranking when the accelerator is depressed fully, indicating a flood condition. Unfortunately, an open circuit earth on the potentiometer type TPS would result in a high output voltage that during cranking would result in a "no engine start” condition as the ECU would suspect you have depressed the throttle fully - Be aware. Contactless TPS units. These are generally found in electronic throttle bodies and are generally not serviced as a separate part. For more information on these units please refer to the Electronic Throttle Body article. Typical circuit description and output results are indicated below.
The Premier Auto Trade Sensor range includes more than 127 Throttle Position Sensors (TPS) from the world’s leading manufacturers, covering over 5 million vehicle applications in Australia and NZ. When you supply and fit products from Premier Auto Trade you can expect a product designed and tested to the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications offering OE form, fit and function. Premier Auto Trade distributes products throughout Australia via a network of specialised resellers and leading automotive groups.
|
Latest News
Tech Tips - Wheel Speed Sensors (WSS) |
| privacy statement terms of use terms and conditions sitemap news |  |